Cloud hosting, also known as cloud computing and on-demand hosting, is an Internet hosting service that can power websites and applications through a network of virtual servers that run on multiple physical computers. Unlike other types of hosting, it’s common for a cloud-powered website to draw computing resources, mainly processing power and disk storage, from multiple virtual servers at the same time. As a result, cloud hosting provides websites and applications with the best performance and uptime when compared to other hosting solutions.
Virtualization sits at the core of cloud hosting and gives it the edge over competing hosting models. With virtualization, a single physical server can be split into multiple virtual servers that operate as independent units. And since each website is powered by multiple virtual servers spread across multiple physical computers, cloud hosting offers unmatched reliability. Moreover, this group of virtual servers forms an elastic cloud platform that allows website owners to instantly add and remove computing resources according to their current needs.
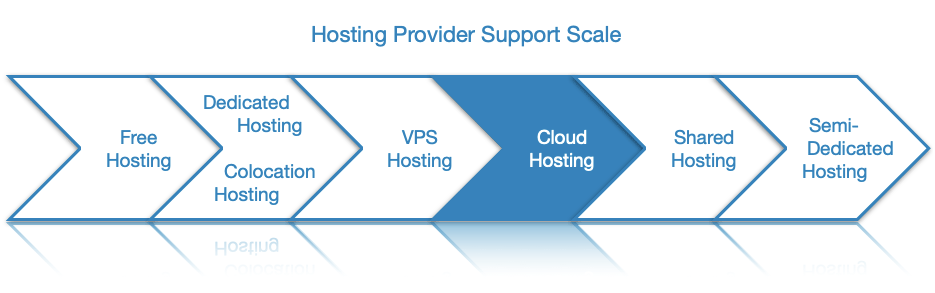
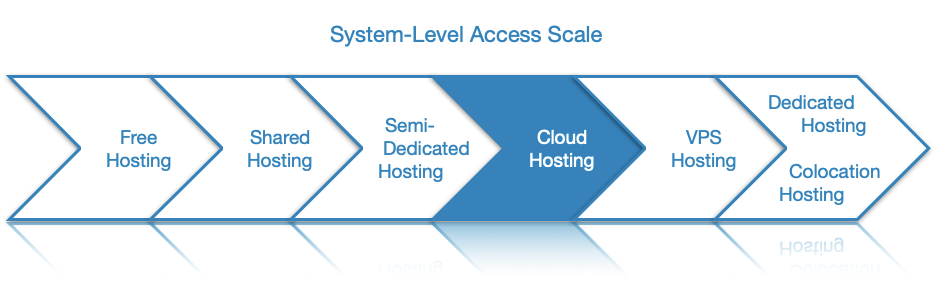
Cloud hosting can be classified as public, private, and hybrid based on the number of users it serves. The public cloud is the most popular and affordable solution and is similar to shared hosting since it allows multiple users to host their websites and applications on the same set of servers. In contrast, the private cloud is dedicated to a single user which makes it considerably more expensive. Lastly, the hybrid cloud is utilized by organizations that opt to use public and private clouds at the same time.
Another unique characteristic of cloud hosting is that it serves as the backbone for several cloud-powered services. These services are the bleeding edge in the online world and they redefine how we use our devices every day. The most popular services are Software as a Service (SaaS), Platform as a Service (PaaS), and Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS). Each service comes with varying degrees of control, but they all offer dedicated system resources.
When it comes to cost, cloud hosting has adopted a pay-as-you-go billing model. In other words, this is a metered service where you only pay for the resources that you have used. The combination of this pricing model with the ability to adjust the number of available resources in real-time makes cloud hosting one of the most performant and cost-effective hosting solutions out there.
Also, check out: Web Hosting: Everything You Need to Know
To learn even more about cloud hosting, continue reading or jump to the section that interests you:
- Advantages
- Disadvantages
- How Does Cloud Hosting Work?
- What Types of Cloud Hosting Are There?
- What Are Cloud-Powered Services?
- Should I Use Cloud Hosting?
- Restrictions and Limitations
- Comparing Cloud Hosting to Other Types of Hosting
- Conclusion
Advantages
Cloud server hosting aims to combine the benefits of all web hosting models into a single package. As such, it comes with multiple advantages, some of which are unique and cannot be found anywhere else. Below, we will list the most notable reasons why you should consider cloud server hosting to power your website or application:
- Cloud hosting provides you with server resources that are not shared with anyone else. Also, in most cases, you would be given a private IP address as well.
- You can manage the number of server resources that you have at your disposal in real-time. The process is usually automated through a control panel and no interaction with the hosting provider is necessary.
- Since multiple virtual servers provide processing power to your website or project, cloud hosting can potentially supply you with more computing resources than any single physical server.
- Another benefit of having a website that is powered by multiple virtual servers is that the chance for downtime is almost zero. Even if one server goes down or is compromised by an attacker, the other remaining servers can pick up the slack and allow your website to remain fully operational.
- Cloud hosting uses a pay-as-you-go pricing model. In other words, you pay only for the computing resources that you have used.
- You can choose between a public cloud that is more affordable or a more secure private cloud. Or you can combine the two models for a hybrid approach.
- By default, cloud hosting is fully managed by the provider, but you can opt for a cloud service that gives you root access if your project or website requires it.
- The cloud sits on the bleeding edge of technology as it serves as the backbone for a new generation of web-based applications and experiences.
Disadvantages
While cloud hosting is one of the most versatile hosting solutions out there, it still comes with several drawbacks. Below, you will find the cloud’s most notable disadvantages:
- While the pay-as-you-go pricing model is an advantage in most situations, an unexpected spike in traffic can result in a noticeably higher bill for that month.
- It is normal for a public cloud server to contain data from dozens or even hundreds of companies. Such servers have become a high-value target for hackers due to the large amount of information they store.
- The cloud hosting provider’s employees usually have full access to the data that is uploaded, especially if you are using a public cloud solution. As such, data loss due to human error and intellectual property theft can occur when using cloud hosting.
- Data stored in the cloud is considered less protected than if it is stored on a private server. As such, you should avoid using the cloud to store confidential information, especially if you are required by law to store it securely.
How Does Cloud Hosting Work?
Cloud hosting is a new type of Internet hosting service that aims to provide site owners with the power of a dedicated server while maintaining the ease of use shared hosting is known for. Each website owner can request the exact amount of computing resources they require, such as processing power, network bandwidth, and disk storage. This is why cloud hosting is often referred to as time-share and on-demand hosting.
The ability of website owners to specify the number of computing resources they need is made possible through a technology called virtualization. Virtualization is a special kind of software that allows one physical computer to be split into multiple virtual servers. Each virtual server functions independently and has its operating system, CPU, RAM, and disk storage.
At this point, you may be seeing some parallels between the cloud and VPS hosting. While the two hosting models do employ virtualization technology, they differ significantly in their execution. When you buy a VPS, you get a single virtual server that is completely under your control. Conversely, with cloud hosting, your website will be powered by multiple virtual servers at the same time.
It is precisely the use of multiple virtual servers that gives cloud hosting the edge over competing hosting models. Instead of using just a single server, each website or project is powered by a group of virtual servers that is often referred to as a cluster or simply as the cloud. These virtual servers are not only spread across multiple physical computers, but they are also seamlessly interconnected and managed by the hosting provider.
Since all virtual servers in a cluster are connected, every server is aware of the computing load that is placed on the rest of the cloud. The benefit here is that once a server is about to become overwhelmed, it can offload some of its tasks to a neighbor that has computing resources to spare. This load balancing minimizes the risk of system freezes due to overloads.
While working with a network of interconnected servers may sound like a daunting task, it is quite simple since the network is completely transparent to the end-user. Instead of having to manage a bunch of virtual servers, you are provided with a unified computing environment that acts like a single computer. This cloud-based computer can supply you with potentially unlimited computing resources such as processing power and disk storage. Moreover, it is common to be given a private IP address as well as to be completely independent of the other websites that the cloud hosting provider may serve.
Simplified server management is just one of several great advantages cloud hosting has over its competition. Another notable advantage is that the cloud is used to enable the next generation of web-based applications and services. The most notable cloud services are:
All of these services offer best-in-class uptime which is made possible by utilizing multiple virtual servers to power a single site or project. As such, if you have a website or application that must run at all times, cloud hosting is your best option.
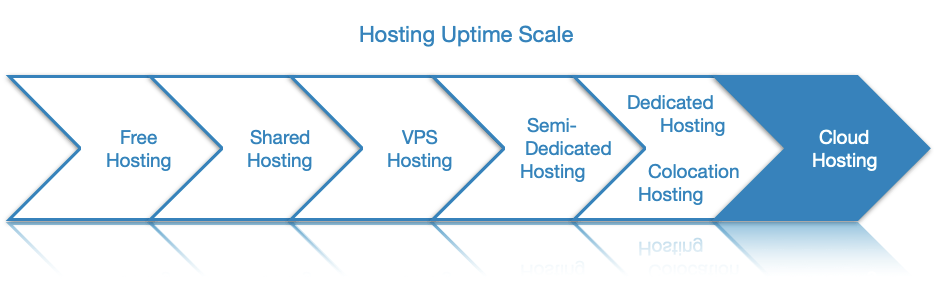
Hosting providers achieve this increased uptime by equipping each virtual server with all necessary software to keep your website or project running. So even if one virtual server fails, the remaining servers that are already powering your website will compensate for its loss. In the meantime, the hosting company can quickly provision a brand new virtual server, configure it with all necessary applications, and add it to the pool of virtual servers that power your website or project.
This method of replacing failed server instances works well in most cases, such as a hardware malfunction of the underlying physical computer or even when a virtual server gets hacked. Since there are other virtual servers already powering your website or project, you will not experience downtime. Instead, you may notice longer loading times while the new server instance is prepped for operation.
While setting up a brand new virtual server with all necessary applications may sound like a labor-intensive process, it is quick and seamless. That is because the hosting provider has other virtual servers that are already configured and are working properly. All the hosting provider needs to do is to make a copy of a working virtual server and upload it to the newly created instance.
The ability to clone a virtual server is great for quickly configuring new server instances, but this convenience comes at a privacy and security cost. You should be aware that in most cases the hosting provider’s privacy policy will grant them complete access to all of your data. Thanks to this access, the hosting provider can not only clone your servers when needed, but they may also provide this information to law enforcement and other government bodies upon request.
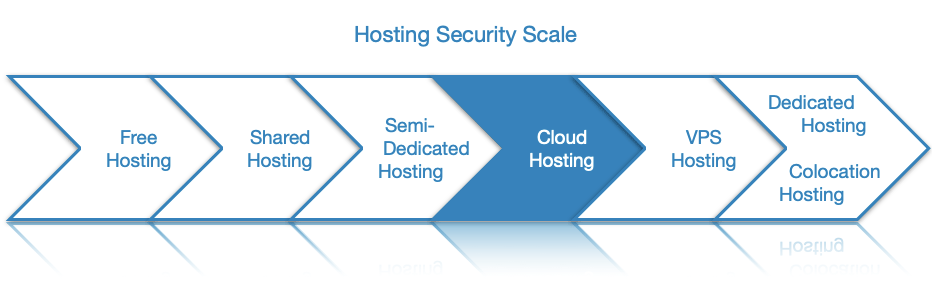
Moreover, it is common for public cloud hosting providers to store the data of hundreds or even thousands of companies on the same set of physical servers. As such, these servers have become a high-value target for hackers since overtaking a single physical server can provide data on dozens of companies.
That said, hosting providers minimize the risk of a security breach by employing state-of-the-art protections such as firewalls, antivirus programs, and internal network scanners that can detect invaders and other unusual activity. So, if you decide to use cloud hosting for your website or project, you should be aware that there’s a small possibility to suffer intellectual property theft as well as data loss due to human error or a cyber attack.
Privacy and security concerns aside, having a hosting plan that exclusively employs virtual servers has another unique advantage – it gives you the ability to adjust the number of computing resources on demand. In other words, you can add and remove system resources such as processing power, RAM, and disk storage per your current needs. Due to this increased flexibility, the cloud is often described as an elastic hosting solution.
What characterizes cloud hosting as elastic is the fact that you can not only add system resources but can also remove them when they are no longer needed. What is more, these changes take effect almost immediately and do not necessitate any downtime.
Adjusting the number of available resources is usually an automated process and you do not need to contact your hosting company at all. Instead, you simply need to use their control panel to make the desired changes. Some hosting providers even go a step further by allowing your cloud to automatically request or release computing resources when certain thresholds are reached.
At this point, you may be wondering how the cloud hosting company can ensure that there are additional server resources available to you when you need them. In most cases, this is accomplished using a multi-tenant hosting model. This is a model where the hosting provider makes a large pool of computing resources available to all of its clients. These resources are mainly processing power, memory, and disk storage.
When a website sees a spike in traffic, it appropriates some of these additional resources to keep up with the increased demand. Later, when the traffic returns to normal, the website can release these extra resources, so they can be used by someone else. Since the entire process of requesting and releasing resources is likely automated, the cloud hosting provider has little to no involvement. Instead, the hosting company just needs to make sure that there are enough extra resources available at all times.
Due to its elastic nature, cloud hosting gives you the ability to tap into practically unlimited computing resources on demand. Large cloud hosting providers do not cap the amount of processing power, RAM, or disk space that you can provide for your website or project. And thanks to the fact that cloud hosting is comprised of multiple virtual servers, it has the potential to supply you with more processing power than any single physical server.
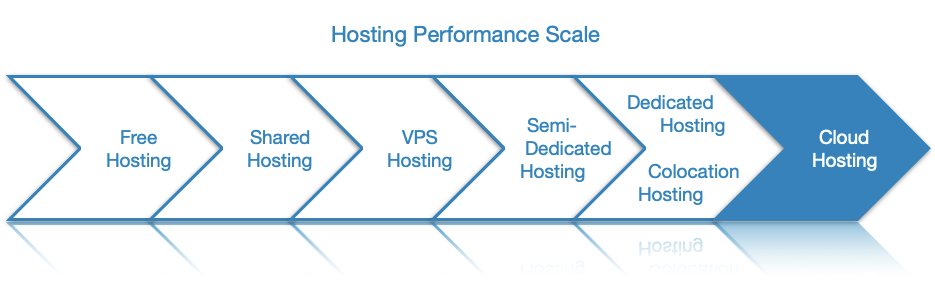
Since the number of computing resources that you use can vary daily, cloud hosting companies employ a pay-as-you-go pricing model instead of a flat monthly or annual fee. In that sense, billing is carried out in a way similar to utility companies such as your electricity provider. With a pay-as-you-go service, you pay only for the resources that you have used.
Most cloud hosting providers calculate your resource usage by simply keeping track of the processing power, RAM, disk storage, and network bandwidth that you have consumed. Other providers, however, may monitor your usage in more abstract terms. This is most common with purpose-built cloud hosting solutions. For example, you may be billed based on the number of active users on your site or the number of requests that your application makes to the cloud-powered back end.
Overall, cloud hosting is more affordable than higher-tier hosting solutions like dedicated server hosting. That said, there is one notable disadvantage when it comes to the cloud’s pricing model. If your website or application experiences a surge in traffic, your resource utilization for that period will spike as well. As a result, you can expect a higher bill for that month. With conventional hosting, on the other hand, you always pay the same price, regardless of your actual usage.
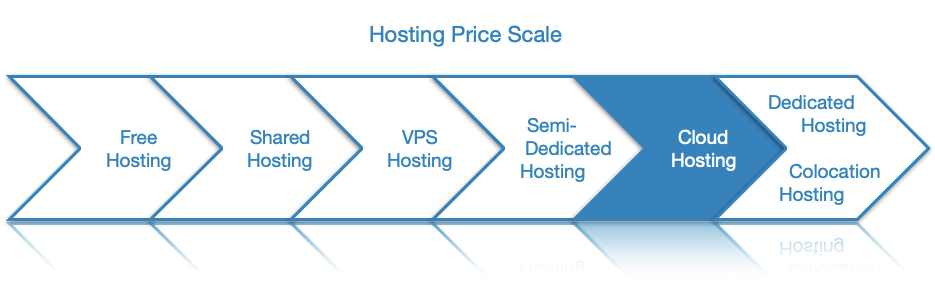
One additional factor that can significantly influence the cost of cloud hosting is the number of companies powered by a single server cluster. If the cluster provides processing power to multiple websites and applications belonging to multiple individuals and organizations, then you need to only pay for a fraction of the server cost. Conversely, the price increases considerably if you have an entire server cluster that is dedicated just to you. We will discuss these different types of cloud hosting in the next section.
What Types of Cloud Hosting Are There?
Cloud server hosting can be classified as public, private, and hybrid based on the number of organizations it serves. Below, we will examine each cloud type in greater detail.
Private Cloud
A cloud is characterized as private if it serves a single individual or organization. As you might imagine, the cost of a private cloud is very high, but having a cluster of virtual servers dedicated to you comes with some unique advantages. The two main benefits are a higher level of control and better overall security.
Since the cloud is built specifically for you, it can be customized so it performs as efficiently as possible. Such customizations may be denied if you are using a general-purpose cloud that acts as a one-size-fits-all hosting solution.
The other main advantage private cloud hosting has is its increased security. This added protection comes from the fact that no other individuals and organizations utilize the same cloud infrastructure. Moreover, large organizations often deploy private clouds on their premises, so they can control who has physical access to the servers.
Public Cloud
As its name implies, the public cloud is designed to accommodate the websites and applications of multiple organizations at the same time. Consequently, it is much more affordable when compared to its private counterpart.
From a technical standpoint, public and private hosting are nearly identical. The biggest difference between the two is the fact that public hosting is less secure and may not be suitable for storing or processing sensitive information. What is more, public clouds tend to store data from hundreds or even thousands of companies. This makes them high-value targets for hackers.
Public cloud hosting is a good fit for organizations that wish to benefit from the tremendous data storage and information processing potential of the cloud, but cannot afford or do not need a completely private hosting solution. If your company handles sensitive information that is regulated by law, then you must make sure that your public cloud hosting provider meets all of the storage and security requirements.
Hybrid Cloud
The hybrid cloud is not a distinct type of cloud hosting. Instead, it simply denotes that a website or application utilizes public and private clouds at the same time. Other hosting combinations can be classified as hybrid cloud hosting as well. For example, you can choose to get a virtual private server and combine it with a public cloud. Or you can get a dedicated server or colocation hosting and use it in combination with your public cloud.
The hybrid cloud is mainly used to overcome the shortcomings of the public cloud. More specifically, it is common for organizations to store all sensitive information on a private hosting solution and only send small pieces to the public cloud for processing. That way sensitive information can be kept safe on a private server while still taking advantage of the computing power offered by public cloud hosting.
Hybrid cloud hosting will be a good fit for you if your organization holds highly sensitive information that cannot be stored on the public cloud. Also, the hybrid model is a good solution for projects that require an immense amount of processing power that cannot be supplied by a single server.
What Are Cloud-Powered Services?
Cloud hosting is different from other hosting models because it enables and powers a whole new generation of web-based software and services. These cloud services are considered the cutting edge in the online world and are rapidly changing the way we use the web and computer programs in general.
Thanks to cloud hosting, companies and individuals can use full-fledged, desktop-class software through thin clients. A thin client is a program that allows you to connect to a remote resource and use it. Web browsers and email programs are good examples of thin clients. Some applications, especially those that run on mobile devices, are usually powered by a server on the back-end and as such, they can also be considered thin clients.
Cloud-powered applications running through thin clients are becoming increasingly common in our everyday lives. In fact, it is possible that you are already using a few web applications running on cloud services and you may not even realize it. Good examples of applications that can run on the cloud are Google Docs and the Spotify web player. These cloud-powered apps are just as performant and feature-rich as their traditional desktop counterparts.
What is more, web-based apps are more secure than conventional programs since all security patches are applied server-side from the moment they are released. In other words, when you load a cloud-based application through a web browser or another thin client, you are always using its latest version.
Cloud-powered apps can truly run the gamut of computer software. You can use cloud-based applications at work, at home, and even for playing video games. Not only that, but the cloud serves as the foundation for web-based development environments where software engineers can build and deploy their custom applications. These applications can later be used by their clients or the general public.
In the following few sections, we will take a closer look at the three most popular types of cloud-powered services: Software as a Service, Platform as a Service, and Infrastructure as a Service.
Software as a Service
Software as a Service, or SaaS for short, is perhaps the most important cloud-powered service since it is widely employed by companies to deliver desktop-class functionality and experiences through a web browser or another thin client. The great thing about Software as a Service is that there is seemingly no limit to the types of applications that can be run.
SaaS enables everything from office and productivity software to communication and collaboration applications and even cloud-based gaming. Google Docs and Slack are good examples of SaaS productivity apps while services like Google Stadia and Microsoft xCloud are SaaS products that allow you to play high-end games through a thin client like a web browser. Since all processing happens server-side, SaaS technology lets you use programs and games on low-powered devices that do not meet the computing requirements to run these kinds of applications natively.
In general, SaaS products are purpose-built and as such, it is common for cloud hosting providers to track software usage in more abstract terms. For example, the hosting company can count the number of daily active users, tally up the total amount of time users have spent using the cloud-powered app, or keep track of the number of requests that are made through the application to the cloud back-end. In contrast, the conventional way of determining server utilization is to simply record all CPU, disk space, and bandwidth usage for a given month.
When it comes to consumer-level customization, SaaS products are usually quite limited. In most cases, users are allowed to personalize how the SaaS app works for their accounts, and rarely do customers can adjust how the app functions for other users. In the next two sections, however, we will discuss two other cloud-powered services that allow greater flexibility and customization by the end-user.
Platform as a Service
While Software as a Service is more business- and consumer-oriented, Platform as a Service (PaaS) is mainly geared toward software developers and companies that wish to deploy and use their custom applications. Cloud hosting companies that offer Platform as a Service would simply provide you with a development environment. You can then use this development environment to either build an application from scratch or upload an app that you have previously developed.
One thing to keep in mind when buying a Platform as a Service is to make sure that the cloud hosting provider fully supports your preferred programming language. Also, the hosting company may opt to support only a few select frameworks and libraries to keep their service from becoming too bloated. In a similar vein, only a few database types may be supported. As such, you must make sure that the hosting company can fully satisfy all of your project’s requirements before signing up for their service.
As you might imagine, PaaS offers a greater level of control when compared to SaaS. As a PaaS user, you can fully manage the application that you have built or uploaded. Additionally, you may be granted a certain level of control over the development environment itself. That said, you will not have root-level access and you will not be able to install arbitrary software on the platform.
Some of the more notable Platforms as a Service are Heroku, Microsoft Azure, and AWS Elastic Beanstalk. Such services are popular among developers since they can significantly reduce the time needed to build an application by quickly providing preconfigured development and deployment environments.
Infrastructure as a Service
While SaaS and PaaS have a narrow focus and are more restrictive from the onset, Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) is one of the most flexible cloud-powered services. With Infrastructure as a Service, you are provided with one or more virtual machines where you can run your website or project.
The great thing about IaaS is that you have complete control over the virtual machines that you are provided with. You are free to add and remove software packages as you see fit. What is more, you can even pick your preferred operating system. The only thing that you are not allowed to manage and modify is the underlying cloud infrastructure as it can only be managed by the cloud hosting provider.
Overall, Infrastructure as a Service is a good option to consider if you require a Platform as a Service, but you cannot find a cloud hosting provider that can supply you with all frameworks and technologies that your project requires. Good examples of IaaS providers are Rackspace, Google Compute Engine, and Digital Ocean.
Should I Use Cloud Hosting?
First and foremost, you should consider using cloud hosting for any website or application that must run at all times. Since your project will be powered by several virtual servers at the same time, it will be accessible even if one of those virtual servers fails.
Additionally, cloud hosting is a great option for projects with unpredictable resource utilization. Since the cloud is an elastic hosting solution, you can provide additional processing power when it is needed and scale back when things return to normal. Doing so will save you money since you will only be paying for the computing resources that you have used instead of having to buy expensive hardware that is capable of handling your highest possible computing load.
Cloud hosting is also a prime hosting candidate if your project is too demanding for a single server to handle. Large websites such as social networks or video-sharing platforms may struggle to run smoothly on a single server no matter how powerful it is. Also, if your project is very resource-intensive, to begin with, a cloud-powered solution might be the best fit due to the cloud’s ability to scale up its resources indefinitely.
The cloud may not be the best hosting solution for you if you need to store confidential information. This is because cloud hosting is generally less secure when compared to dedicated and colocation hosting. You can work around this issue by opting for a private cloud. Alternatively, you can go with a hybrid cloud solution where you use a public cloud for information processing and a dedicated server or a VPS for data storage.
Restrictions and Limitations
The most important limitation that you need to keep in mind while using cloud hosting is that the hosting provider can access your stored information at all times. In most cases, the hosting provider’s privacy policy will have a clause stating that they may share all of your uploaded data with third parties to comply with requests from government and law enforcement bodies.
As such, you should not use the cloud to store confidential information or data that you are legally obligated to protect. If your website or project does contain confidential information, then you should consider storing this data on a private cloud or a dedicated server instead.
Apart from these privacy limitations, you should keep in mind that most cloud hosting providers will have a zero-tolerance policy when it comes to copyrighted materials. Additionally, most hosting companies will refuse to offer you services if your project or website includes adult content. As such, it is important to communicate with your hosting provider and ensure that your website or application will not violate their terms of service.
Comparing Cloud Hosting to Other Types of Hosting
Without a doubt, cloud hosting is one of the more unique hosting solutions out there. That said, using the cloud to power your website or project may not be the best decision in all situations. In the following few sections, we will compare cloud server hosting to all other major hosting types.
Cloud Hosting vs Shared Hosting
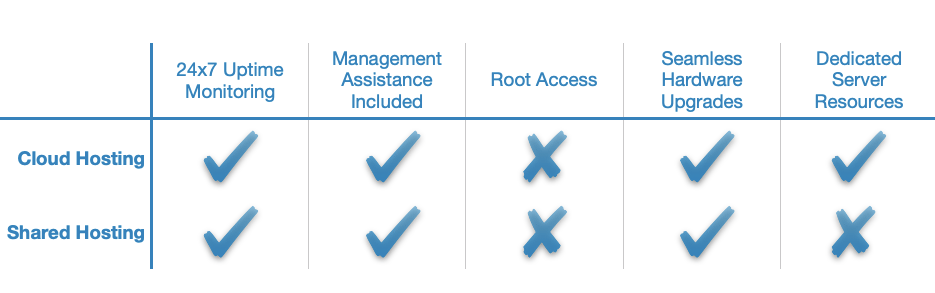
Cloud hosting and shared hosting use two very different approaches when it comes to power websites. A cloud-powered website draws computing resources from multiple virtual servers while shared hosting often accommodates dozens or even hundreds of sites on a single server. This has two major consequences:
- Shared hosting is much more affordable since multiple users share the cost of a single server. As such, you can buy a premium shared hosting plan without breaking the bank or you can even get free web hosting and start building your website without any upfront investment.
- Cloud hosting is much more reliable since multiple virtual servers power a single website. So if one virtual server goes down, the site will remain operational. In contrast, if a shared hosting server goes down, so do all websites that are hosted on that physical server.
Another point to consider is the fact that shared hosting is considered a managed hosting service and it is fairly easy to use. Most cloud hosting plans, on the other hand, are self-managed and offer many more features which could be confusing at first glance. Therefore, shared hosting might be a better fit for individuals without a lot of technical experience, and for organizations that lack a dedicated IT department.
Cloud Hosting vs Semi-Dedicated Server Hosting
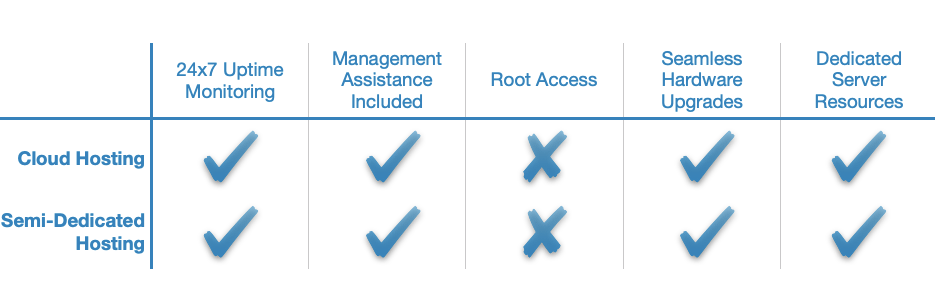
When compared to semi-dedicated hosting, cloud hosting has numerous advantages. It is considered more flexible and more powerful. It is also much more reliable in terms of server stability and uptime. Also, since semi-dedicated hosting is very similar to shared hosting, all of the points that we made in our cloud hosting vs shared hosting comparison still hold true.
On the other hand, buying semi-dedicated hosting may be the right choice if you are looking for a hosting solution that is not as expensive while still providing a considerable amount of computing power. In addition, semi-dedicated hosting should be easier to use since there aren’t as many options cluttering the control panel interface when compared to the cloud.
Cloud Hosting vs Colocation Hosting
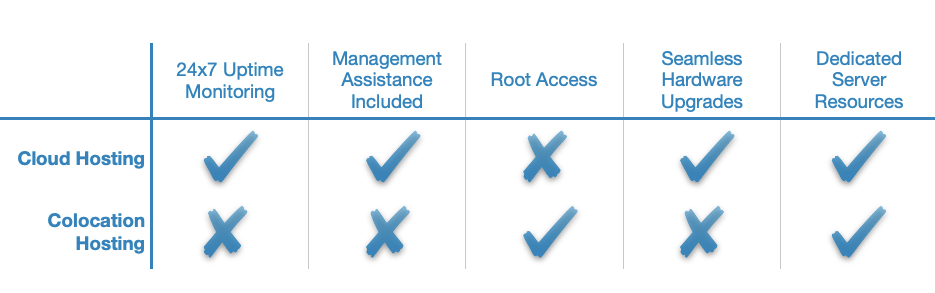
Cloud and colocation hosting differ profoundly in the way they are set up and operate. The cloud is created and maintained by the hosting provider and you simply buy as much processing power and disk storage as you need. If you get colocation hosting, on the other hand, you are responsible for everything from getting and installing the server hardware to configuring your hosting environment. The colocation data center is only responsible for providing uninterrupted power, cooling, and broadband access.
Colocation hosting will be a good fit for you if you already own the server hardware that you wish to use. Another great advantage of colocation hosting is that you are fully in control of your data. As such, colocation hosting is one of the most secure hosting options out there.
Conversely, you should opt for cloud hosting if your website or project requires varying amounts of processing power at different times. Also, the cloud may prove to be a more affordable option when you compare it to buying colocation hosting and high-end server hardware. Lastly, the cloud generally requires less technical knowledge to operate.
Cloud Hosting vs Dedicated Server Hosting
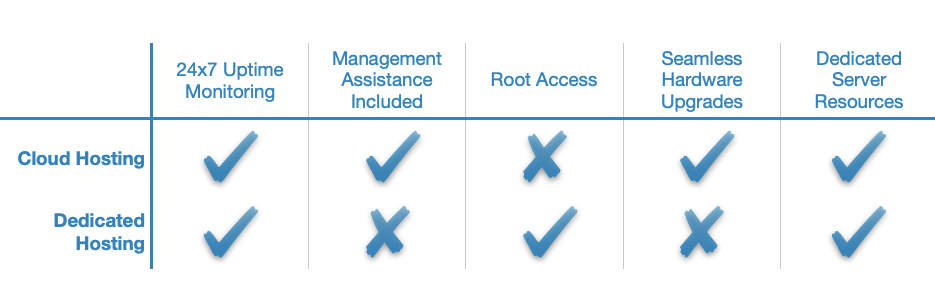
Both cloud and dedicated server hosting are considered high-end hosting solutions, however, they have been delineated thanks to a few notable differences. First and foremost, dedicated server hosting offers much better privacy and security. This is because when you purchase a dedicated server, no third parties will have access to it.
Cloud hosting, on the other hand, can offer better uptime and overall stability since it uses multiple servers to power a website rather than a single, albeit dedicated, server. The use of multiple virtual servers also means that cloud hosting has the potential to outperform even the most powerful dedicated hosting solutions.
You should consider getting dedicated server hosting if your website or project will require a considerable amount of processing power at all times. Also, a dedicated server will be a better choice for organizations and individuals that wish to store confidential information.
Lastly, dedicated and cloud hosting is not mutually exclusive. A popular hybrid cloud hosting model involves using a public cloud for information processing and a dedicated server for data storage.
Cloud Hosting vs VPS Hosting
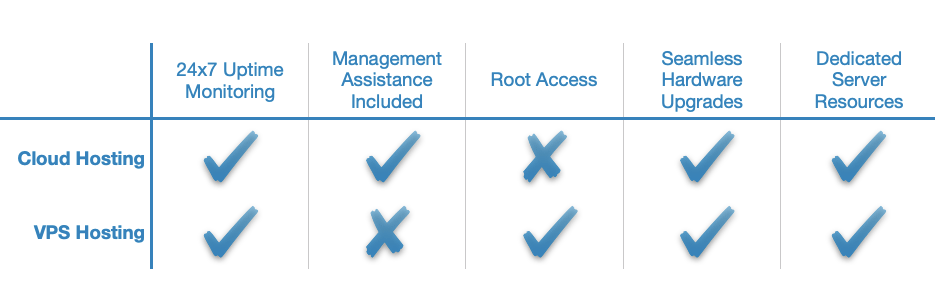
From a technical standpoint, cloud and VPS hosting are very similar. This is because both hosting models exclusively employ virtual machines to deliver hosting services. However, each web hosting solution takes a different approach.
With VPS hosting, each client is given root access to a single virtual private server. So, if you decide to buy a VPS, you will be provided with a virtual server where you can install any application that you need. You will even be able to choose your operating system.
With cloud hosting, on the other hand, your website will be powered by multiple virtual servers at the same time. This will provide you with best-in-class uptime and you will have the ability to adjust your resource usage on the fly depending on your current needs. On the downside, some cloud-powered services do not offer full root access. As such, you should ensure that your website or application will be fully supported before purchasing the cloud hosting package.
Conclusion
Without a doubt, cloud hosting is superior to other existing models in many respects. It delivers the best possible uptime and it has the potential to outperform any other hosting solution because it uses a cluster of virtual servers to power a single website or project.
What is more, cloud hosting is more diverse and accommodating than conventional hosting since the cloud is packaged into several distinct services. Thanks to these services, individuals and organizations can choose the level of customization and complexity that they are comfortable with.
On top of all that, the cloud offers the fairest way of charging for hosting since you only pay for the resources that you have used. That said, pricing is the only real drawback of cloud hosting. The cloud is still in its nascent stage which is why it is still not as widespread and affordable as regular shared hosting.
