The 403 Forbidden error message is an HTTP status code that can occur when a client tries to retrieve a resource from a server and the server denies access to the requested resource. This requested resource can be anything from a webpage to a PDF document, a multimedia file, or even an executable application.
To learn more about what error 403 Forbidden is, what causes it, and how to fix it, continue reading or jump to the section that interests you:
- What Is a 403 Forbidden Error?
- What Causes the 403 Forbidden Error?
- What Are the Differences Between 403 Forbidden and 401 Unauthorized?
- How Can I Fix a 403 Forbidden Error?
- Conclusion
What Is a 403 Forbidden Error?
The 403 Forbidden error message is an HTTP status code that belongs to the 4xx series of messages that signify a client-side issue. HTTP error 403, in particular, signals that the server has received and understood the client’s request, however, it is rejecting to fulfill it since the client lacks the permissions that are necessary to access the resource.
When a server encounters a request it cannot fulfill and has to respond with a 403 error code, it will actually send back a whole webpage that explains the error to the user. The user’s web client would display this error page just like any other webpage and it will look exactly the same regardless of the specific web browser or operating system that is used.
Some website owners might opt to tweak the appearance of the 403 Forbidden webpage to better match the overall style of their website. If you are using our hosting services and wish to customize the page that your visitors get when they encounter a 403 error code on your website, you need to be using one of our Virtual Private Server plans.
Speaking of customizations, different webserver applications have slightly different wording for the error. Below, you will find the most common variations of the 403 Forbidden error message:
- 403 Forbidden
- Forbidden
- HTTP 403
- HTTP Error 403 – Forbidden
- HTTP Error 403.14 – Forbidden
- Error 403
- Error 403 – Forbidden
- Forbidden: You don’t have permissions to access [directory] on this server
- That’s an error.
What Causes the 403 Forbidden Error?
At its core, a 403 Forbidden error is generated whenever the server rejects a client’s request because it deems that the client does not have the necessary permissions to access the resource. This can be a very powerful security measure that keeps confidential information private, but it can also be set up by mistake and wreak havoc on your website. In this section, we will examine the various ways a server can be set up to generate a 403 error code.
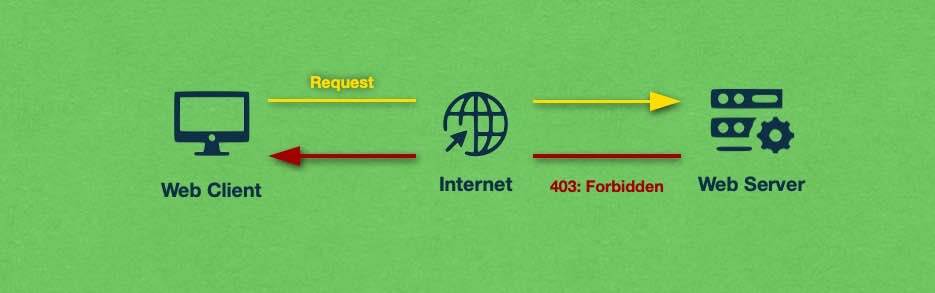
The first scenario that we will examine involves the permissions for the files and directories on the server. A novice webmaster can easily make the permissions too restrictive which would result in unwanted HTTP 403 errors. Of course, the permissions can also be set low on purpose so that access to the resource is intentionally denied.
Next, we should mention that the .htaccess file can be used to generate 403 errors by instructing the webserver application to disallow access to certain sections of the website. Again, this can be done on purpose or by mistake.
Another common cause of error 403 is when the website owner has disabled directory browsing for their server and they have not specified a page that should be displayed instead of the file structure. Directory browsing is often seen as a security and privacy risk, so it is common for it to be disabled, but it is also common for webmasters to forget to specify an alternative page.
Website owners may choose to target visitors with specific IP addresses and geographical locations and completely prohibit access to their website. If such a restriction is placed, the visitor would get a 403 error code for all URLs that belong to the website.
Lastly, we should mention that our hosting platform may produce a 403 Forbidden error in an attempt to protect against security threats and to ensure that our platform is not hosting websites that violate our Terms of Service.
For example, if you fail to log into the back-end of your website multiple times in quick succession, our security software will interpret this as a brute-force attack against your website and will proceed to temporarily ban your IP address, which could result in a 403 error message. This protection is active on all of our shared hosting plans including our free website hosting plan, our premium shared packages, and the semi-dedicated servers.
Further security measures are placed on our free hosting platform which could deny access to your website and show a forbidden error instead. The most important restriction that you need to keep in mind should you decide to get free hosting from us is that your website may be blocked automatically if it contains a word or a phrase that is commonly found on phishing websites. For more information on these restrictions, you can check our article on what restrictions there are on our free hosting platform and how to resolve them.
What Are the Differences Between 403 Forbidden and 401 Unauthorized?
The 403 Forbidden and 401 Unauthorized error codes are very similar in nature. Both of them belong to the 4xx category of HTTP status codes which indicates a client-side error. However, there is one notable distinction between the two messages.
While both codes indicate that the client does not have the proper permissions to view a given resource, the 401 Unauthorized error implies that access was denied due to incorrect or missing authentication on the client’s part. As such, if the client makes another attempt to access the resource and ensures that a proper WWW-Authenticate field is included in the request header, then chances are that the 401 error code will be resolved and the client will be permitted to view the resource. We cover HTTP error 401 Unauthorized in much greater detail in a separate article.
In contrast, the 403 Forbidden error indicates that the server’s decision to deny access to the resource is final. With a 403 error code, it is implied that the client has already successfully authenticated itself with the server, yet it still lacks the permissions necessary to view the resource.
How Can I Fix a 403 Forbidden Error?
The 403 Forbidden error can be caused by a lot of different issues which we outlined earlier. In this section, we will focus on providing a fix for the various problematic scenarios. We will show you how to fix a 403 error code when you come across it while surfing the web and we will also provide guidance on how to resolve the error if it is occurring on your own website.
How Can I Fix a 403 Forbidden Error on a Third-Party Website?
To begin with, we’ll explore what your options are if you come across a website that displays a 403 Forbidden error message. Overall, there isn’t much you can do since you do not have access to the server that powers the website. That said, below you will find the actions that are most likely to fix the issue.
The first thing you need to do when you stumble across a 403 error code is to reload the page after double-checking the URL, especially if you have typed it manually. If you are trying to access a specific file, make sure that you are entering the correct file name along with the file extension. Otherwise, the webserver will interpret the end of the URL as a directory and will look for a folder that has your file’s name.
The next most probable cause that can be fixed on the client-side is if your web browser has an outdated cache and/or cookies. If this is indeed the case, then your web browser would be making requests for resources that no longer exist. To fix this issue, simply clear your browser’s cache and cookies and then try reloading the page. If you are not sure how to clear a web browser’s cache and cookies, you can read our guide on the subject.
Some websites are poorly configured and may be showing you a 403 Forbidden error message when, in fact, they should be showing a 401 Unauthorized response instead. If the website allows registrations, create an account, log in, and then try accessing the restricted webpage one more time. We covered the differences between a 403 Forbidden and a 401 Unauthorized error codes a bit earlier in this article.
If all of the above steps have failed in resolving the 403 error code, your last option is to contact the website owner directly and inform them of the issue you are experiencing. In most cases, the website owners will be eager to resolve the matter as quickly as possible.
In very rare cases the website owner might inform you that the 403 error is not caused by an issue on their end. If you find yourself in this scenario, your last course of action would be to contact your Internet Service Provider (ISP) as it is possible that your IP address has been blocked for some reason.
How Can I Fix a 403 Forbidden Error on My Own Website?
Now that we have exhausted the options that are available to you if you encounter the 403 error message on a third-party site, we will take a closer look at the changes you can make if your own website is experiencing this issue.
The most common reason why a webserver might return a 403 Forbidden error message is when the requested resource’s permissions are set very low and that prevents the server from sharing the resource with the client. To fix this, you should use an FTP program or an SSH client to connect to your website and then set your directory permissions to 755 and your file permissions to 644. And if you are using our free hosting, paid hosting, or semi-dedicated server platform, you can use our integrated File Manager to set your file and folder permissions.
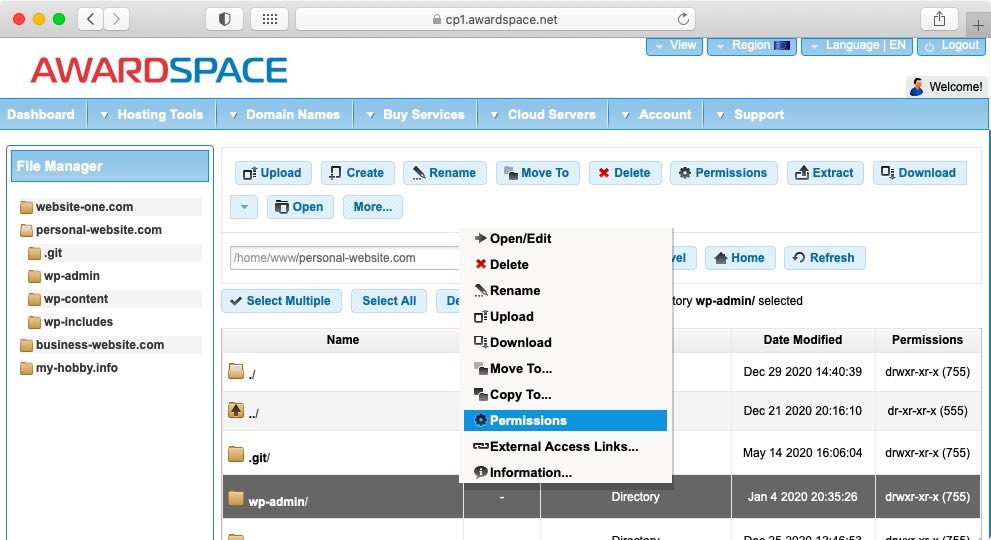
Another common issue that generates 403 Forbidden errors is a faulty .htaccess file. You should disable the .htaccess file in order to find out whether it is indeed the culprit. And if you are using a Content Management System like WordPress, you should also create a new .htaccess file that contains the default directives for the CMS. We have a separate article where we show you how to fix .htaccess-related to issues in a WordPress site.
403 error codes can also be generated by a web server that is configured to disallow directory browsing. When the server is not allowed to display the content of directories and a visitor makes such a request, they will receive a 403 HTTP response code. You can resolve this issue in two ways:
- The easier option is to simply make sure that all directories contain an index file. If a directory doesn’t have an index file already, you can create an empty
index.htmlfile there. That way, the server will return a blank page to the visitor who requests the contents of a directory instead of returning a 403 Forbidden error that is caused by the directory browsing restriction. - The second way to resolve the issue is to configure the server to display a custom error page instead of returning error 403. This approach requires more technical knowledge, but it is also more preferable since you can return a more meaningful page to the visitor.
If you are using a CMS like WordPress it is not uncommon for a plugin to start causing 403 errors when it is buggy or improperly configured. So, to find out whether a plugin is a culprit in your case, you should disable the plugins folder by renaming it to something like plugins-disabled. If your website no longer displays 403 errors, then one of your plugins is indeed the root cause.
Error code 403 can also occur if you have recently switched from one hosting company to another and you have forgotten to update your domain’s nameservers. If this happens, then your website will still load using your old hosting company’s servers and if your account with them expires, then you will likely start seeing errors like 403 Forbidden. To fix this issue, simply update your nameservers so they point to your new hosting provider and then allow a few hours to pass for the changes to take effect.
Speaking of hosting providers, if you are using our free hosting platform you may run into 403 Forbidden error messages whenever our security system detects words and phrases on your website that are commonly used for phishing. You can resolve this issue by either removing the forbidden words or upgrading to one of our paid hosting packages where these restrictions are not enforced.
If all of the above steps have failed, and you are still receiving a 403 Forbidden error on your site, you can contact your hosting provider for additional assistance. In most cases, they would be able to pinpoint the exact reason why your website is displaying this error code.
Conclusion
It is not uncommon for websites to display a 403 Forbidden message from time to time. In most cases, this happens because the visitor does not have the permissions necessary to view the file or webpage that is accessed. However, there are also times when access is denied due to a mistake in the server configuration. As such, if you receive a 403 Forbidden error in a place you don’t expect it, it is always a good idea to reach out to the website owner and let them know that you are experiencing this issue.
And should your own website experience a 403 error message, we recommend resolving it by going through the steps outlined earlier in this article. In the unlikely event that our recommendations fail to resolve the forbidden error, you should go ahead and contact your web hosting company for additional assistance.
