Domain names make browsing the Web far easier and faster for users. Each registered domain is comprised of several parts that give more information to the user about what the website is about and what they can expect to see once they open it.
In the next paragraphs, you will read about the different parts of a domain name, what they do, and why are they important.
Understanding the Different Parts of Domains
Domain names are comprised of 4 domain parts. 3 of these are mandatory, and one is optional.
These parts are:
The idea behind the components of a domain name is to give as specific information as possible.
Let’s see more in detail.
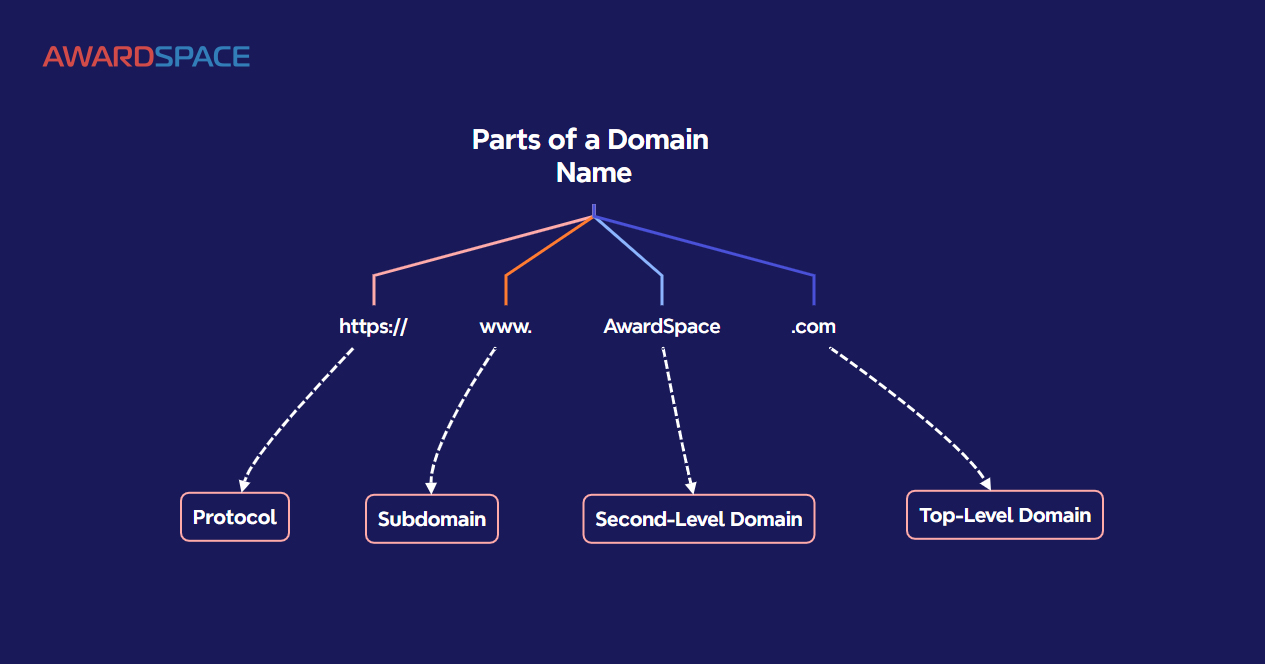
1. HTTPS Protocol
HTTPS is the secure version of HTTP.
HTTP, an abbreviation for Hypertext Transfer Protocol, is the foundation on which the communication between clients and web servers is made possible.
At its core, HTTP contains a set of requirements for formatting and processing computer data, called a protocol. This protocol is what computer devices use to exchange various types of information between themselves.
In the example, https://ExampleWebsite.com, the part “https://” indicates that HTTP is being used to transfer the data, associated with this domain name.
2. Second-Level Domain
Let’s keep with the example from the previous point– https://ExampleWebsite.com
This domain name is comprised of 3 domain parts – the http// protocol, and two parts, separated by a dot. These parts are “ExampleWebsite” and “.com”.
In this example, the part “ExampleWebsite” is called a Second Level Domain (SLD) and can be comprised of any combination of symbols, words, and phrases you wish, as long as this combination is unique, compared to all other domain names.
When choosing your domain name (and customizing your second-level domain), you can use your brand’s name, your name, or any prominent word or phrase that is common in the industry your website will be about, or anything else.
Here are some tips you can have in mind when choosing a SLD for your website:
- Keep it short and simple.
- Keep it memorable.
- Make sure it is available and not protected from use.
- Add a keyword, so you add a kick to SEO.
3. Top-Level Domain
Top-level domains, or TLDs, known also as domain extensions, are the components that stay on the right of the second-level domain and are separated by a dot.
For example, in http://ExampleWebsite.com, the top-level domain is “.com”.
You can’t register a domain name without including the TLD part.
TLDs give more information about what the website, associated with the domain is all about. With TLD, you can inform your potential site visitors that your website is a governmental one, a company one, educational, informational, or anything else.
There are numerous types of top-level domains, categorized depending on what type of information they give about the website they correspond to. Here are some examples:
Generic TLDs. These top-level domains are commonly used and grant information about what your website is about. Examples include:
- .com – an extension used for the majority of websites.
- .net – Intended for websites in the tech industry. Today .net is widely used by various websites.
- .org – This TLD is primarily used by non-profits, charitable organizations, and NGOs.
- .edu – Specific TLD, used by American educational institutions.
- .gov – USA-exclusive TLD, reserved for the websites of USA federal institutions.
- .co – An alternative to .com, this TLD is widely used by startup companies and businesses operating in the high-tech industry.
Generic-Restricted Top-Level Domains (grTLD). Such top-level domains can only be used after certain requirements are met.
IANA, the global organization that oversees IP address allocation globally, has set a list of rules that you should abide by to receive the right to use such TLD.
grTLD examples include:
- .biz
- .name
- .pro
Sponsored Top-Level Domains (sTLD). sTLDs are special types of top-level domains and are sponsored by private organizations.
Sponsored top-level domains are used by organizations that operate in the same industry and share similar themes.
The specific thing about sTLDs is that the sponsoring organization has the final word on whether the requirements to receive such top-level domain are met.
Examples include:
- .museum
- .edu
- .mil
Country-Code TLDs. These top-level domains indicate that the given website, corresponding with that domain name is focused on a specific country and its institutions, territory, and organizations that operate in such regions.
Examples include:
- .au – Australia
- .ca – Canada
- .uk – United Kingdom
- .fr – France
- .ie – Ireland
Test Top-Level Domains. Such domains are reserved for testing and development activities.
What is specific for testing top-level domains is that they can’t be registered via a Domain Name System. This means that you can freely use such top-level domains without risking any future conflict with the domain name.
Examples include:
- .test
- .example
- .invalid
- .localhost
4. Subdomain
Subdomains are optional prefixes that are added to the domain name to separate certain types of content on your website in a different website, which different websites remain within the boundaries of your main domain.
Subdomains are placed to the left of second-level domains and are separated by a dot.
An example of a subdomain is this:
blog.ExampleWebsite.com
in this domain the subdomain is “blog.” – it is placed right next to the second-level domain (ExampleWebsite), on its left side, and gives a certain type of information as to what type of information the website associated with this domain contains.
In the example above, as the name suggests, blog.ExampleWebsite.com would lead to a separate website, containing the entire blog section of the http://ExampleWebsite.com website.
Other uses of subdomains might be creating an online store (store.ExampleWebsite.com), a test environment for web developers (test.ExampleWebsite.com), or separating the mobile version of a given website from the desktop version (mobile.ExampleWebsite.com).
Conclusion
Subdomains are comprised of 3 mandatory parts and one optional. Each part gives information on what the website is about and performs a specific function.
Check also:
