A VPS, which stands for Virtual Private Server, is a type of Internet hosting service that provides you with the functionality of a dedicated web server while maintaining the affordability of a shared hosting plan. When you purchase a VPS hosting plan, you get a virtual machine with full root access, allowing you to use programs and scripts that cannot be run in a shared hosting environment.
Hosting providers who offer virtual private servers are able to maintain low pricing by housing multiple virtual servers inside one physical computer. This is very similar to the way regular shared hosting works. But unlike shared hosting, where all users share a common pool of computing resources, the physical server that powers VPS instances uses a technology called a hypervisor. The hypervisor is able to set the amount of processing power, RAM, and storage that each virtual private server can utilize.
Another standout feature made possible by the hypervisor is the elastic cloud platform which has been adopted by many of the top VPS providers out there. Thanks to the elastic cloud platform, which is also used by AwardSpace, you can adjust the number of computing resources your VPS uses in real-time. So, it is possible to buy a VPS that is not overpowered and later upgrade it with more RAM, a better processor, and additional storage when the need arises.
As we briefly mentioned earlier, a VPS can run a lot of applications that are not compatible with most shared hosting environments. However, with this greater freedom also comes greater complexity. In other words, managing a VPS is not as easy as using a shared hosting account. As such, a certain level of technical experience is necessary. Fortunately, most hosting providers offer VPS assistance packages in order to help you with your server’s configuration and maintenance.
Also, check out: Web Hosting: Everything You Need to Know
To learn even more about VPS hosting, continue reading or jump to the section that interests you:
- Advantages
- Disadvantages
- How Does VPS Hosting Work?
- What Is VPS Hosting Used For?
- Choosing the Right VPS
- Getting Help in Managing a VPS
- Restrictions and Limitations
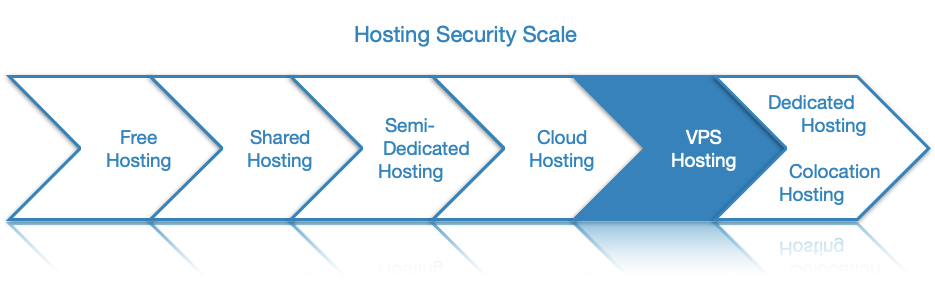
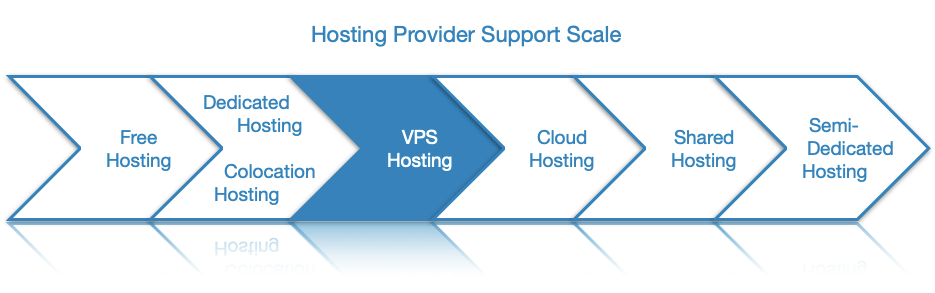
- Comparing VPS Hosting to Other Types of Hosting
- Conclusion
Advantages
VPS hosting has some great advantages over other types of hosting, both in terms of hardware performance and software capabilities. Below, you will find the most notable benefits of owning a virtual private server:
- A new virtual private server can be deployed in a matter of minutes.
- VPS hosting will provide you with dedicated CPU, RAM, and disk space that are not shared with others.
- Additional processing power and memory can be added to the server on demand.
- The VPS hosting provider may allow your server to “borrow” computing resources from other VPS owners when these resources are not in use.
- Virtual private servers are more reliable than shared hosting.
- Each VPS comes with a private IP address.
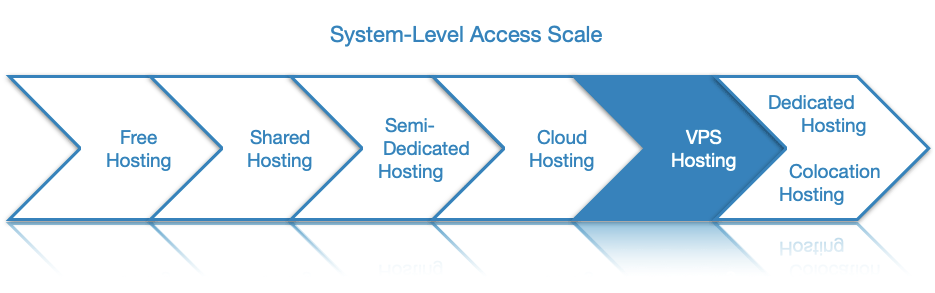
- You will be given full superuser/root access over the virtual private server.
- You can choose which operating system powers your VPS.
- Any application or software package can be installed on your VPS.
- It is possible to install a control panel like cPanel for easier server management.
- Thanks to root access, you can harden your VPS security by installing custom firewalls, and antivirus software, and restricting access through an IP whitelist.
Disadvantages
There isn’t a perfect hosting solution and VPS hosting is no different. Below, you will find the most significant drawbacks that come with a virtual private server:
- One physical server runs multiple VPS instances which can have security and privacy implications, especially if you are storing confidential information.
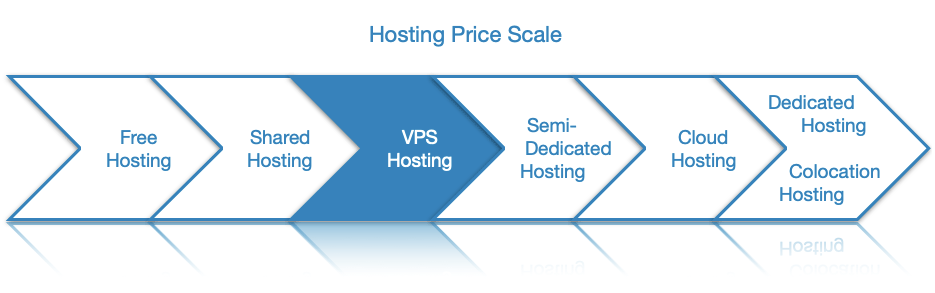
- While not as expensive as a dedicated server, a VPS costs significantly more than a regular shared hosting plan.
- Knowledge about server administration is required to properly manage your VPS.
- In most cases, the VPS owner is fully responsible for operating and maintaining the virtual private server.
How Does VPS Hosting Work?
The main premise behind VPS hosting is to provide users with greater control over their hosting environment. This is achieved by using virtual machines which are sophisticated programs that run on a computer. But unlike single-purpose applications like a calculator, a virtual machine has its own operating system and can run its own applications. You can think of this as a computer within a computer.
The great thing about virtual machines is that they are self-contained and are completely isolated from the host computer and its operating system. In other words, even if a virtual machine freezes, the rest of the system will remain operational. What’s more, this isolation gives you the freedom to reboot or even reinstall your VPS at any time without affecting the host computer or any other virtual private servers that may also be running on it.
The concept of isolation is taken even further with a technology called a hypervisor. You can think of the hypervisor as a flight dispatcher at an airport. But instead of helping airplane pilots during takeoff and landing, the hypervisor tells each virtual server how many resources it is allowed to use. These resources are processing power, which is measured as available CPU cores, RAM, and disk space.
The hypervisor’s ability to dynamically allocate computing resources across multiple virtual servers forms the basis of the elastic cloud platform. When your VPS runs on an elastic cloud platform, you can quickly add extra computing power the moment your server needs it. Some VPS hosting providers even go one step further by allowing you to “borrow” unused computing resources from neighboring virtual servers when your VPS is overloaded.
One of the biggest advantages a virtual private server has over shared hosting is that you are given full root access and can install any package that your website or application may require. In most cases, you would need to manually carry out the installation of these additional packages. This makes VPS hosting much more complex to run and maintain when compared to a shared plan. The silver lining here is that most hosting providers will offer some sort of VPS assistance if you require it, either as a one-off payment or a recurring subscription.
There are literally thousands of packages and applications that you can install and use on a virtual private server. As such, no control panel can cover all the potential features a VPS has to offer. Instead, you leverage the full power of a virtual server through the command line. The command line is a text-based user interface where you type in commands and send them to the server for execution.
To send commands to the VPS, you need a command-line application. Linux and macOS users can take advantage of the built-in Terminal app while Windows users can use the built-in Windows PowerShell or a third-party program like PuTTY. The commands are sent to the VPS over the web using the secure shell (SSH) protocol.
Working with the command line can be intimidating, especially if you have never used it before. Fortunately, it is possible to install a graphical user interface on the VPS. If you do so, you will be able to use a remote desktop protocol like RDP or VNC to connect to your virtual private server and use it as a regular computer. That said, the use of graphical user interfaces on servers is generally frowned upon since these interfaces are very resource-intensive and may noticeably decrease the performance of the VPS.
What Is VPS Hosting Used For?
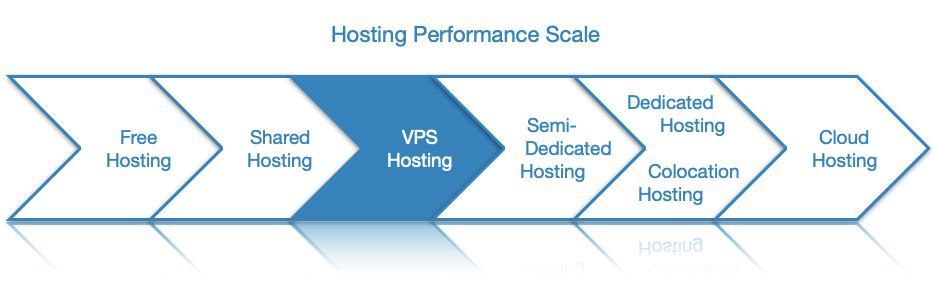
VPS hosting sits in the middle of the hosting spectrum, both in terms of performance as well as cost. That is why a lot of small and mid-sized companies opt to rent a virtual private server. With a VPS, you get more control and computing resources when compared to a shared hosting plan.
For many site owners, this greater control is the standout feature offered by VPS hosting. When you buy a VPS, you will be given full root access to the virtual server and you will have the ability to install and use custom scripts that cannot run in a shared hosting environment. In fact, it is not uncommon for website owners to upgrade to VPS hosting just to get this increased level of control.
If you have a custom-built website that uses technologies that are not available in a shared hosting plan, you should definitely consider upgrading to VPS hosting. Another compelling reason to upgrade is if you are seeking a hosting solution that offers better performance, privacy, and reliability when compared to a shared hosting plan.
There are other reasons to get a VPS as well. Thanks to the wide breadth of applications available to install on a virtual private server, it can be used for much more than just hosting a website. Below, we will list some of the more noteworthy uses of a VPS other than web hosting:
- A private mail/contacts/calendar/messages/notes server. If you do not trust the cloud, you can use a VPS to send and receive emails. You can even enable syncing functionality for text messages, contacts, calendars, reminders, and notes.
- A game server. You can use a VPS to act as a private server for multiplayer games.
- Private cloud storage. It is possible to create your own Dropbox-like service for syncing and backup purposes.
- Application back-end. Smaller-scale desktop and mobile applications can use a VPS as their back-end. In other words, the VPS can provide the information which is then presented through the app to the user.
- A general-purpose computer. If you get a VPS that is powerful enough to run a graphical user interface, your server can become a remote computer used for day-to-day tasks like creating documents and running business/productivity software.
- A developer server. A VPS can be used for compiling code, running continuous integration testing, and running computationally-intensive processes for long periods.
- A private VPN. With a VPN you can have a more secure connection when you browse the web using open networks like cafes and airports.
At this time it is important to note that not all VPS hosting providers allow all of these uses for a virtual private server. As such, you should check your hosting company’s Terms of Service or contact them before starting to use their VPS for one of these non-standard tasks.
Choosing the Right VPS
While there are plenty of companies that offer VPS hosting, not all virtual private servers are the same. There may be differences in both the hardware setup as well as the software availability. What is more, your choice of a VPS hosting company also matters
In the following few sections, we will provide some tips on how to rent a virtual private server that will best suit your needs.
Choosing the Right VPS Hosting Provider
The first decision on the path to getting a virtual private server is to choose your VPS hosting provider. There are three important metrics you should keep in mind while evaluating each hosting company:
- The VPS hosting provider must be able to supply you with a virtual server that is powerful/affordable enough for you.
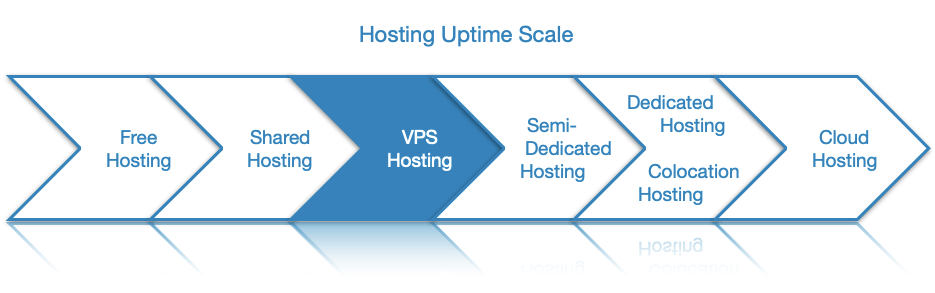
- Next, the VPS hosting provider must have an excellent uptime record, preferably at least 99.9% uptime on average.
- Lastly, you should check the VPS provider’s Service Level Agreement (SLA) for information on how much technical support you are entitled to when using their VPS services.
Here at AwardSpace, we guarantee that your VPS will be running at least 99.9% of the time. Moreover, we aim to provide high-performance virtual private servers at an affordable price. There is even an option to instantly add extra computing resources should you need them. So, if you decide to buy a VPS from us, you will be getting a rock-solid server that will not break the bank. What is more, if you ever run into any issues with your server, you can purchase a VPS assistance package and our professional System Administrator team will help you in a matter of minutes.
Choosing the Right Hardware
Even though VPS instances are virtual by nature, they still need a physical server to power them. Therefore, the hardware specifications of the underlying physical machine are still an important factor to consider. A good rule of thumb is to make sure that the physical server uses components that were introduced no more than three years ago.
Unlike shared hosting, where all users compete for the same pool of resources, each VPS comes with its own set of resources that are not shared with anyone else. The main hardware parameters you should keep in mind are the CPU, RAM, storage, and network bandwidth. We will examine each of those in greater detail in the next few paragraphs.
When it comes to CPU performance, most VPS hosting providers allocate virtual CPU cores to each VPS instance. Basic VPS packages often come with a single core while more expensive options allow the utilization of multiple CPU cores at the same time. As you might imagine, older CPU models are less powerful, so make sure that the physical server uses a state-of-the-art CPU to begin with.
RAM is another important VPS characteristic. More RAM means that more processes and applications can be run at the same time. Currently, the best performing RAM is DDR4, so you should look for a VPS hosting provider that offers it. ECC RAM is a special kind of memory that minimizes the risk of data corruption. ECC RAM is much more expensive and is mainly used on servers that carry out financial transactions and perform other high-value operations.
Next, we will discuss storage. There are two broad types of storage: SSD (Solid-State Drive) and HDD (Hard Disk Drive). SSDs are faster while HDDs offer more space for the same price. If you are seeking the ultimate performance in disk read/write speeds, you should look for a hosting provider that offers an SSD NVMe option which is even faster than a regular SSD. It is not common for a single VPS to use both SSD and HDD at the same time, so you will most likely need to choose one type of storage and use it across your entire server.
Lastly, we will look at bandwidth and traffic. Bandwidth is the maximum amount of data your server can send or receive at any given moment. Traffic, on the other hand, is the sum of all used bandwidth over a given period. When picking a VPS plan, your bandwidth should be at least 50Mbit/s and your package should include at least 1TB of traffic per month.
Now that we have gone through the main hardware characteristics of a virtual private server, we can discuss one of its primary advantages over the competition – seamless scalability and upgrade potential. These advantages are facilitated by a technology called the hypervisor which manages the resources available to each VPS instance. The management happens in real-time without having to power down the VPS. This yields three great benefits for VPS owners:
- No downtime during upgrades.
- Near-instant upgrades.
- The ability to add processing power when you need to and scale back when you don’t.
Choosing the Right Software
When it comes to software, every VPS is a blank slate, so it can be built from the ground up, allowing the virtual server to satisfy the owner’s specific needs. All of this customization starts with the operating system. Broadly speaking, there are two main OS choices: Linux and Windows.
Linux is an open-source operating system that comes in many different flavors called distributions. Each distribution comes with a different set of programs and features. Some distributions are jacks of all trades, having adequate support for multiple tasks, while other distributions are purpose-built with just one or two tasks in mind.
The vast majority of Linux distributions, such as Debian, Ubuntu, CentOS, Fedora, Unix, FreeBSD, and Slackware, are provided free of charge. That said, you can also find paid Linux versions, such as Red Hat Enterprise and SUSE Enterprise. In most cases, you don’t need to buy a paid distribution to have a stable and reliable server.
Your other choice of operating system is Windows. Microsoft developed a special version of Windows called Windows Server. This is a paid operating system that is supported by many VPS hosting providers. It is normal for a Windows-based VPS to be more expensive due to Microsoft’s licensing fees.
So how do you decide between Linux and Windows as your operating system of choice? Most of all, you should consider the type of applications that you will be running on the server. If you will be using Microsoft technologies such as MS SQL Server or ASP.NET, you should go with a Windows VPS. Conversely, if the underlying technology for your project or website is cross-platform, such as PHP, MySQL, Java, ASP.NET Core, NodeJS, and others, you should probably get a Linux-based VPS. Not only will a Linux-based VPS be cheaper, but you will find many more VPS hosting providers who support it.
Once you have settled on an operating system, it is time to start thinking about the software that will be running on the virtual private server. Aside from the mission-critical packages that power your website or project, an important area to consider is security.
Virtual private servers are one of the most secure hosting options out there. However, this holds true only when the server is properly configured. A poorly managed VPS can have multiple vulnerabilities and may be exposed to multiple outside threats. As such, hardening your VPS security should be one of your top priorities.
You should consider setting up enhanced security measures such as programs for scanning the VPS for hackers and other invaders. Closing unused ports is also a good idea. Moreover, if you are accessing your VPS from a single static IP address, you should whitelist it and deny access to all other connections that attempt to take control of the server. Lastly, you should add an anti-virus program that regularly scans your VPS for worms, trojans, and other threats.
Getting Help in Managing a VPS
By default, VPS hosting is an unmanaged hosting solution. This means that the owner is responsible for setting up applications, optimizing performance, and applying security patches. Consequently, a fair amount of technical knowledge is required to properly operate a VPS. Failure to do so may lead to security vulnerabilities and suboptimal performance.
Fortunately, VPS owners are not left completely on their own. In most cases, VPS hosting providers will offer some sort of assistance package where you can hire the company’s system administrators to perform a specific task on your VPS. Some hosting providers even go a step further by allowing you to sign up for a managed VPS hosting service. With a managed service, you pay an annual or monthly fee and for that, you have 24/7 access to support personnel who will not only monitor your VPS for issues but will also carry out OS updates and apply security patches. If you own a managed VPS, it is also likely that the hosting provider will help you in setting your website or project to run on the server.
Restrictions and Limitations
While a VPS offers a great deal of freedom when it comes to the kind of applications and websites that you can run, most VPS hosting providers will still impose certain restrictions through their Terms of Service. As such, it is important to read these legal documents before signing up for a VPS with a specific company.
In most cases, hosting providers will prohibit the use of IRC as it can lead to DDoS attacks against their network infrastructure. Additionally, adult and copyrighted content will be prohibited. Lastly, you will likely not be able to run network scanners and web crawlers as these can be very taxing on the provider’s bandwidth capacity.
If you plan on using your VPS for a non-standard activity it is always best to contact the hosting provider and ask if this activity is OK with them. If you do not do so, you may find yourself in violation of their Terms of Service and may be penalized in some way.
Comparing VPS Hosting to Other Types of Hosting
While VPS hosting is definitely one of the more versatile hosting solutions out there, it is not the best choice in every scenario. In the following few sections, we will compare a VPS to the other major types of web hosting.
VPS Hosting vs Shared Hosting
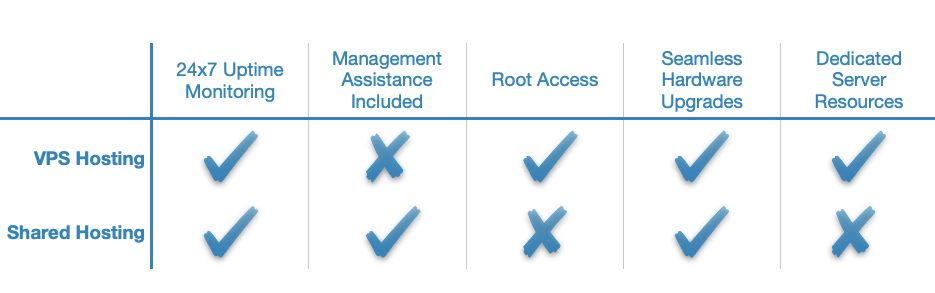
VPS and shared hosting are similar in that multiple site owners use the hardware of a single physical server to power their websites. However, there is one profound difference between the two resource-sharing models. While on a shared hosting plan everyone competes for the same processing power and memory, with a VPS, each site owner gets a portion of the physical server’s resources allocated to them. As such, when you buy VPS hosting, you will get greater stability since you are guaranteed a certain level of performance.
That said, VPS hosting is not for everyone. Having a VPS is considerably more expensive than purchasing a shared hosting account. If you are just starting your website and do not get a lot of traffic, you can save money by buying a premium shared hosting plan or even just getting a free shared hosting account.
While a VPS can cost twice as much as a shared account, the virtual server can provide you with full root access which is something you cannot get with a shared hosting account. Thanks to root access, you can run applications on your VPS that simply cannot be run in a shared environment.
Another advantage VPS hosting has over its shared counterpart is increased security. Each virtual private server has its own operating system and is completely isolated from other virtual servers that may be running on the same machine. So even if a neighboring VPS gets hacked, your VPS should not be negatively affected. What is more, thanks to the root access a VPS comes with, you can implement additional security measures, such as custom firewalls and antivirus packages.
The only major downside to VPS hosting is that you need to have advanced Linux/Windows administration skills to use it to its fullest potential. Moreover, the need for technical knowledge is exacerbated by the fact that most VPS packages are unmanaged, meaning that you will not receive free technical assistance from the VPS hosting provider. Shared hosting, on the other hand, is a form of managed hosting and comes with full technical support and an easy-to-use control panel.
VPS Hosting vs Semi-Dedicated Server Hosting
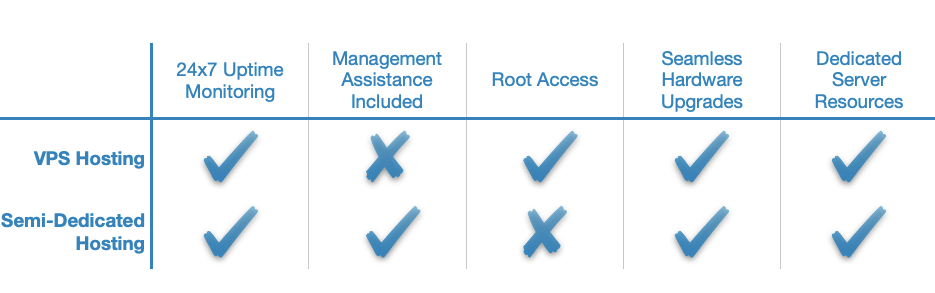
While semi-dedicated hosting and virtual private servers are both classified as mid-tier hosting solutions, each brings its own unique strengths. Semi-dedicated servers tend to be more powerful and easier to use. However, they are also much more restrictive when it comes to the number of technologies and frameworks that can power your website.
VPS hosting, on the other hand, tends to be less powerful than a semi-dedicated server, but it is more affordable, secure, and provides you with much greater control over your hosting environment. As a result, you are able to install and run any application that your project requires. What is more, plan upgrades tend to be smoother with a VPS package and often occur without any downtime.
A virtual private server will be a better fit for you if you already know how to manage a server and wish to have full root access. On the other hand, you should buy a semi-dedicated web server if your website is based on a popular content management system like WordPress and you are more concerned with better performance rather than greater control over the server.
VPS Hosting vs Dedicated Server Hosting
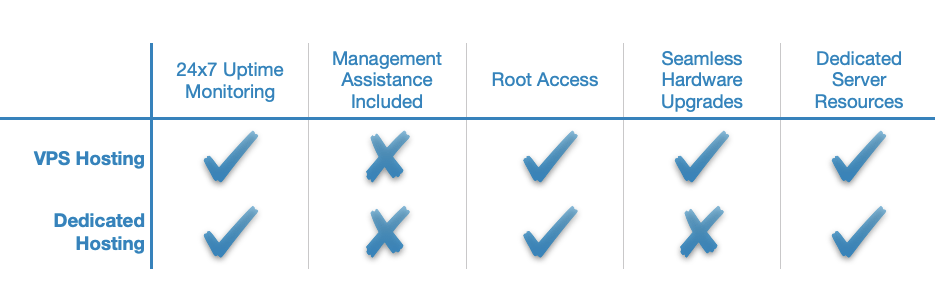
From a functionality standpoint, VPS hosting and dedicated servers offer you the same level of control over the server. You can install applications, run custom scripts, and configure every hosting parameter to your liking. The major difference between the two hosting types comes from the fact that with a VPS you own a virtual server that has limited resources available, while with a dedicated server you are renting an entire physical server. As a result, dedicated hosting is much more powerful and it is considerably more expensive.
As we have outlined, a VPS is a software construct while a dedicated server is a physical “bare-metal” machine. Both have unique characteristics which we will explore in greater detail below.
Since virtual private servers are just sophisticated programs, they can be created and destroyed in mere seconds. What is more, some VPS hosting providers like AwardSpace allow you to supply a custom OS image that already contains your needed applications and other parameter settings. So once the operating system image is restored, the VPS will be ready for use without any further setting adjustments. This can tremendously reduce the time needed for deployment.
Another significant advantage a VPS has over a dedicated server is the way upgrades are handled. With a VPS, you can instantly add more computing resources or extra storage space without having to power down the VPS or reboot it. As a result, you can start with an affordable VPS that offers average performance and only upgrade when you need to.
Dedicated server hosting, on the other hand, has its own advantages over VPS hosting. First and foremost, a dedicated server offers performance that no VPS can match. Additionally, dedicated hosting is the most secure type of hosting since you are renting an entire physical server and you are not sharing it with anyone else.
The two main disadvantages dedicated hosting has over a VPS are the high price tag and the fact that hardware upgrades often require the server to be powered down which results in downtime. To avoid such scenarios, dedicated server owners often purchase servers that are powerful enough to handle all requests even at peak utilization times.
Overall, virtual private servers are more convenient and more affordable than their hardware counterparts. As such, you should consider getting a dedicated server only when a VPS can no longer handle the computing load that your website or project requires.
VPS Hosting vs Colocation Hosting
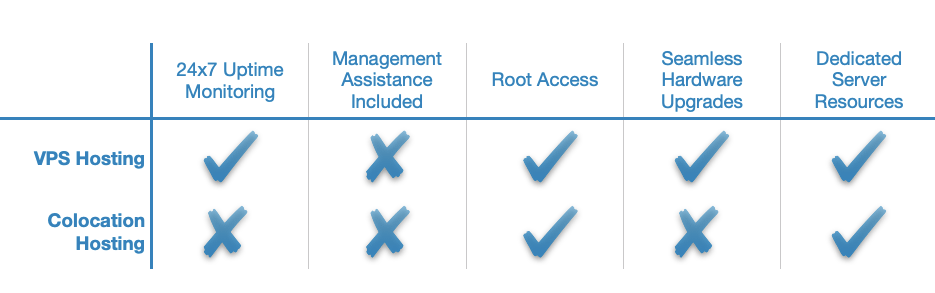
Since colocation hosting and dedicated server hosting are functionally the same, all points that were made in our VPS Hosting vs Dedicated Server Hosting comparison still apply. Colocation hosting diverges from dedicated hosting in that the client is responsible for bringing their own hardware and it offers the highest security of any hosting type. Additionally, colocation hosting clients should implement their own server/application monitoring since the colocation provider will likely only ensure that the server is powered on and will not be checking whether its applications are running properly.
VPS Hosting vs Cloud Hosting
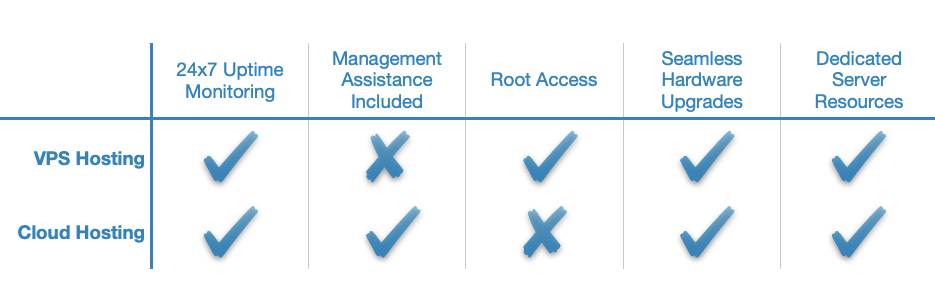
Both VPS hosting and cloud hosting rely on virtualization technology to function. However, each type of hosting takes a unique approach to providing hosting services. With VPS hosting, a single physical server is split into multiple virtual servers which are then assigned to different clients. Conversely, with cloud hosting your computing environment uses the hardware resources of multiple physical servers at the same time.
As a result of this different approach, cloud hosting can supply you with the processing power of multiple physical servers. Moreover, since your applications run on several machines at once, your website or project will continue to run even if one of those machines fails due to a hardware malfunction. In other words, cloud hosting can provide you with the very best possible uptime.
Cloud hosting has one major drawback which is its lower level of security when compared to a virtual private server. Since the cloud utilizes multiple physical machines to power your website or project, this means that your data lives in multiple places at once. This results in an increased risk in case one of these physical machines is compromised.
Conclusion
VPS hosting is one of the most versatile hosting solutions available today. A virtual private server can not only power your website, but it can also act as a mail and calendar server for example. It is truly a jack of all trades and can be used for numerous tasks depending on your computing needs.
If you decide to purchase a VPS, you will find that it is not as affordable as a shared hosting account, but is not prohibitively expensive either. The real limiting factor is that prior experience in server management is necessary in order to properly set up and maintain the virtual server.
In summary, we would recommend VPS hosting to all website owners who wish to be more independent and have complete control over their hosting environment. Adequate technical knowledge is also a must since using a VPS is much more involved than a regular shared hosting account.
