Every one of us should know exactly how Google works. Because if you take the time to think about it, the company has a major role in our everyday life. Even if one is unable to perceive it, due to a lack of interest in the industry, Google is in such a position that allows them to change the web.
Therefore, understanding how the search engine works, will help you foresee what changes may occur, and why the web looks the way it looks.
We live in a time, where it’s early and yet, somehow, trivial to say that our kind is frighteningly interconnected with technology.
Though a lot of people are scared of the possibility that technology will somehow escape our control and thus, overtake our position as dominating species, I feel skeptical about such progress.
When thinking of technology people are scared of losing their jobs, but rarely does someone looks beyond his or her own life. We don’t think about how much the development of new technologies, changes the life of the people, unable to move or even talk.
Google and this type of technology have much more in common than one might think.
To better understand how Google works, let’s find out a bit more about ourselves.
How Does the Human Brain Work?
Throughout most of our history, we didn’t have any idea, how our brains work. Aristotle had the idea that it is something like a cooling system for our lurid hearts.
Although there is a poetic spirit to that claim, it’s just not true. Our heart is a pump for the blood to go where it needs to be – everywhere in our bodies. Thus, it doesn’t play any major role in our comprehension of the world. In fact, the heart doesn’t play any role when it comes to our abilities to move, think, speak, and learn. The only role the heart has, except the one given by Nature, is the one that we gave it – to regulate emotions. Of course, it doesn’t do that, but writers and other artists, made it so that everyone in the world believes that – thus, we say ‘I love you from the bottom of my heart’.
A whole century after the scientific revolution in the 17th century, we figured that the brain is an electric organ.
In that electric organ are your memories, dreams, aspirations, your fears, the way you perceive yourself, your taste of food, music, books, movies, your sexual preferences, ideas, the reasons for you to find something funny, annoying, or offensive. Everything that constitutes you, is in the brain. Including the ability to think, speak, learn, move, sleep, and all of the five senses we have – sight, hearing, taste, smell, and touch.
How all of this works? The easiest way to answer is – through electric impulses. In February 2014 a story appeared in National Geographic magazine. The title was The Secrets of the Brain. Which as of now is available at the National Geographic website.
Without going any deeper, so I won’t spoil your enjoyment of the NG’s article, I want to note that all these electric impulses are going through our brains in a very specific manner. These impulses are regulating every single one of our activities, including the subconscious ones.
The brain does one more thing, we don’t consider that often. Sorting. The brain sorts important from unimportant tasks. A vast number of our activities are made on autopilot – we don’t think about sleeping, moving, tasting, or breathing. And once we perfect a skill, we don’t think about performing it, either. Like driving, or riding a bike.
Our brain is storage for an immense amount of information, with unbelievable sorting power.
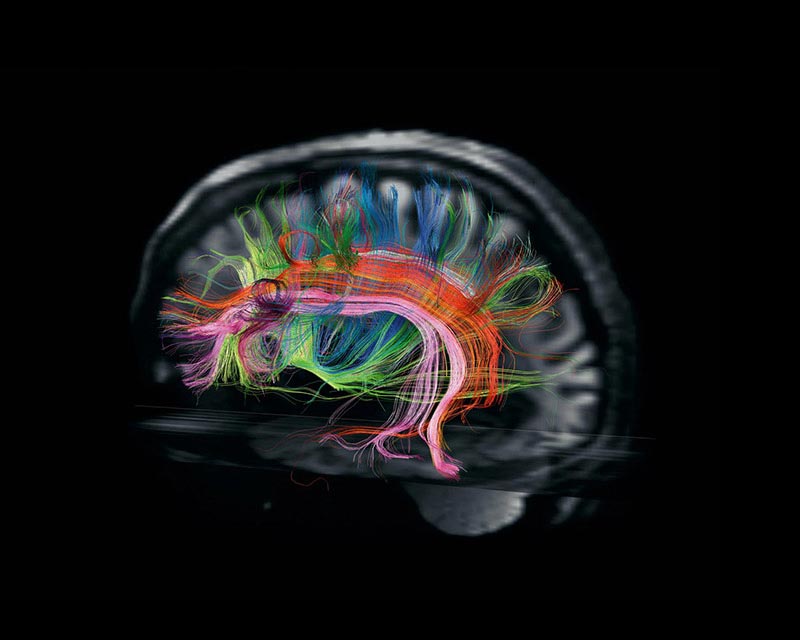
The brain’s many regions are connected by some 100,000 miles of fibers called white matter—enough to circle the Earth four times. Images like this, taken at the Martinos Center, reveal for the first time the specific pathways underlying cognitive functions. The pink and orange bundles, for example, transmit signals critical for language.
Source: National Geographic Magazine – Secrets of the Brain
A (Very) Brief History of Search Engines and SEO
More or less, since the emergence of search engines, like AltaVista, people were trying to figure out their algorithms in order to outsmart them and rank higher on the result pages.
That lead to experiments on both sides. Search engines and digital marketers strived to outsmart each other. And here we are today. Google is giving away information on how to optimize your content to rank higher, and on the other hand, digital marketers are continuing to polish their knowledge and techniques.
As the search engine shows results related only to the query of its users, the results it shows are highly related to the words, we look for. And the first versions of the search engines were ranking websites higher due to the number of times the specific word is present on a website.
Those words became known as keywords.
But once, once the SEOs figured out how the search engines work, they went so far that they started to write keywords in white color on white background. Thus, exploiting the systems to gain the benefit of being in the first place.
This practice became known as keyword stuffing. And, as of now, is forbidden by the Search Engines. The usage of the keyword stuffing practice may result in higher positions in the SERPs for a while, but will eventually lead to a penalty, and probably an impossibility to rank again.
When Larry Page and Sergey Brin created Google, had this major problem – marketers could interfere and spoil the results that the engine’s users were seeing by stuffing the keywords they wanted their website to rank on.
That is why Google crowdsourced, in a way, the ranking of the pages. The Search Engine started to crawl the websites, following the inbound and outbound, as well as internal links, to define who is ‘voting’ who. Thus, Google was able to reckon which websites are important, and which are not.
The more important the links between websites became, the more links emerged. Therefore, the more connected the web became.
Links, of course, existed way before Google, and will, probably, continue to exist, once (if ever) Google melts away.
But the search engine became so important to our everyday life, that it’s hardly possible for the latest to occur.
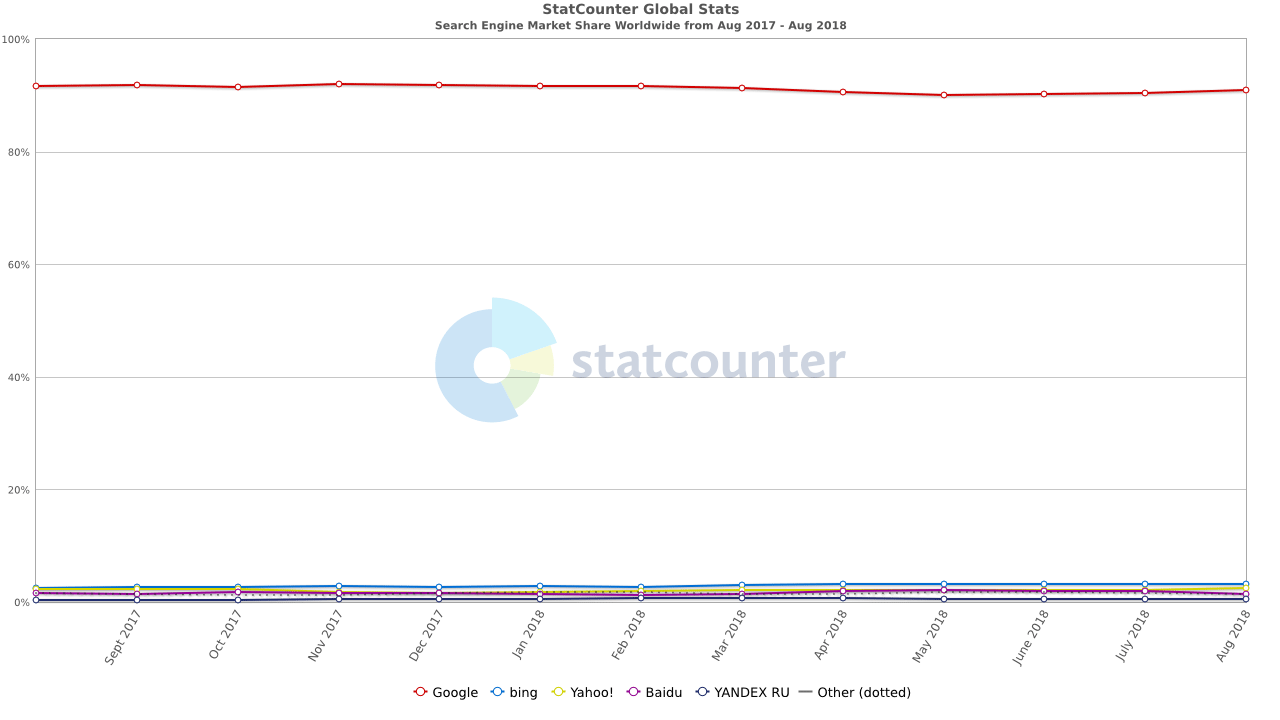
Source: StatCounter Global Stats – Search Engine Market Share
How Google Works
As the search engine market is highly dominated by Google, we’ll refer to the engine, as if it represents all of them. Which is not much far from the truth.
The main purpose of search engines is to present the user with useful information. Thus, they are trying to keep the result pages as clean as possible. No phishing websites, no keyword stuffing, and the fewer articles with ‘thin content’, the better.
To be able to evaluate all the websites on the web, the first thing that Google is doing is crawling the internet. To crawl the web is proving to be a difficult task because. The internet, like the Universe, is not standing still. It is growing, and growing, and growing.
And to give you and me relevant content, the search engines, shouldn’t stop crawling that information. They should know what every page shown on the SERPs consists of. Therefore, the engine will be able to present it to you, once you write the keyword in the search bar.
As Google themselves is sharing:
The crawling process begins with a list of web addresses from past crawls and sitemaps provided by website owners. As our crawlers visit these websites, they use links on those sites to discover other pages. The software pays special attention to new sites, changes to existing sites and dead links. Computer programs determine which sites to crawl, how often and how many pages to fetch from each site.
After the Search Engine crawls a larger part of the Internet, as they are able to, they are organizing the collected information, so that the search engine will be able to present you with the needed information at the right time.
By indexing all the founded content, they “take note of key signals — from keywords to website freshness — and [we] keep track of it all in the Search index.”
To be able to find the right content at the right time, the search engine is sorting the pages. First by topics, and afterward, by relevancy. The measurement of the latest happens through a lot of factors, some of which we’ve covered in our article, dedicated to On-Page SEO.
Conclusion
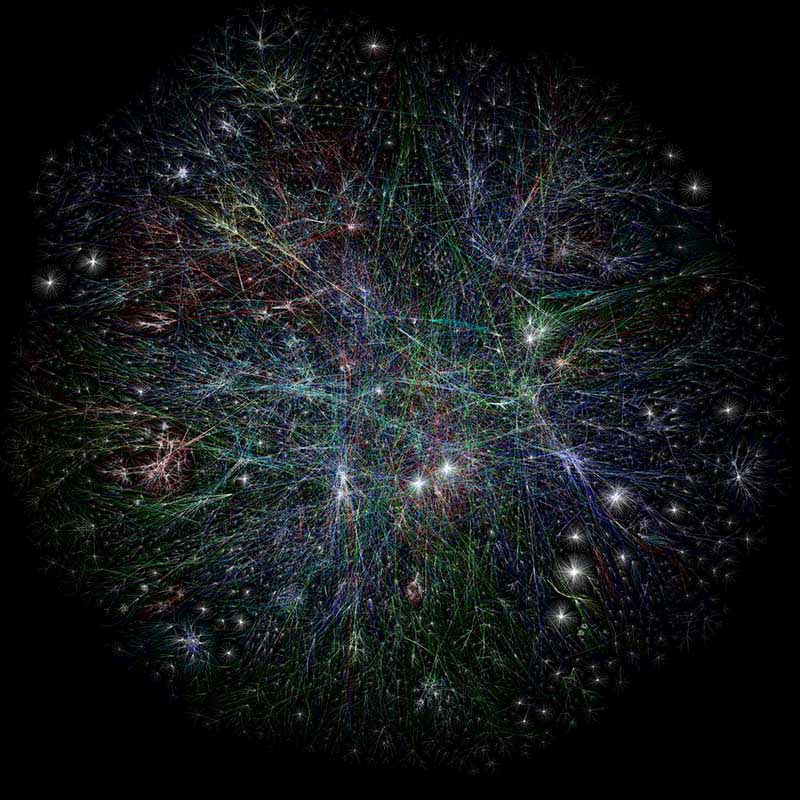
This is the first full Internet map with color and other graphing logic created by The Opte Project.
Source: The Opte Project
Google, as well as our brains, is diving deep into all of the possible connections that it can, just to offer us only these connections that are important.
An interesting observation is how much the relations between all the participants on the Internet, are resembling the network that the “specific pathways underlying cognitive functions” in our brains are making.
If we, somehow compare our brains to the Internet, Google is that part of the brain that takes care of the sorting function. In the same way that you probably don’t want to think about your breathing when hunting, working, eating, or talking, Google takes care of you not seeing websites dedicated to cats, when you are looking for Free Website Hosting.
Maybe we all got it wrong. Maybe when we understand how Google works, we’ll find out that it is not just a search engine. We, the users, are searching. Google is sorting. Making it easier for us to find what we need.
Maybe the right way to think about it is as a sorting engine…